Readwise update
This commit is contained in:
parent
db067f93e2
commit
47bc34093a
12 changed files with 412 additions and 0 deletions
35
Readwise/A guide to design tokens.md
Normal file
35
Readwise/A guide to design tokens.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|||
# A guide to design tokens
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[invisionapp.com]]
|
||||
- Full Title: A guide to design tokens
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[design]] [[dev]]
|
||||
- URL: https://www.invisionapp.com/inside-design/design-tokens/
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=A%20guide%20to%20design%20tokens
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> Design tokens help ensure consistency across different platforms by managing design properties from a single source. They are defined pairs of code and visual properties, like colors and spacing, that can be easily deployed. By using design tokens, teams can streamline updates and maintain a cohesive brand identity without confusion.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
if you established a new data layer on top of your existing design elements ... and managed them from a single place, you could use a system to consistently scale it to all platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, a design token is a design decision: a pairing of the same code and visual properties—design elements you use over and over again in your products—packaged in a format that’s deployable across all platforms. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gb6cqqmf343z3g33y56jkb))
|
||||
|
||||
Each token will be given **a name** that corresponds to a certain design decision/option and the defined **value.** [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gbesf4pcyz7va8f288kq2j))
|
||||
|
||||
are an abstraction layer that makes them **platform-agnostic**. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gbf531ycxc49212f6p6f1r))
|
||||
|
||||
Before any coding is implemented in DSM or your SSoT, designers and developers must agree on:
|
||||
• What should be a token
|
||||
• How those tokens will be used
|
||||
• How those tokens will be named [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gbjas3kb8h0szhxkkj6rss))
|
||||
|
||||
For ease of use, it’s recommended to use Category/Type/Item (CTI) naming conventions to define tokens in a hierarchical tree structure of options and decisions. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gbmfh2rzgrx74f36r0f8s6))
|
||||
> [!note]
|
||||
> This seems like a good way to categorize pretty much anything
|
||||
|
||||
Alias tokens create a hierarchy of options and decisions to control the scope, or intent, of changes. So let’s say you wanted to just change the background color on the buttons. You can create an alias token that reads as an inheritance from the global token as such:
|
||||
Using the earlier alias example – color.background.button.primary – the ‘category’ would be ‘color’. Moving down the tree the ‘type’ would be ‘background,’ followed by ‘button’ as the ‘item.’ [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gbshpy8mqhasnve88440mw))
|
||||
|
||||
31
Readwise/Design Systems 101 What Is a Design System.md
Normal file
31
Readwise/Design Systems 101 What Is a Design System.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|||
# Design Systems 101: What Is a Design System?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Figma]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Design Systems 101: What Is a Design System?
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[design]]
|
||||
- URL: https://www.figma.com/blog/design-systems-101-what-is-a-design-system/
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Design%20Systems%20101%3A%20What%20Is%20a%20Design%20System%3F
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> A design system is a collection of standards and components that ensures consistency and efficiency in digital products. It helps designers work faster by providing reusable elements, allowing them to focus on more complex challenges. Implementing a design system can improve collaboration and streamline workflows across teams, making the design process smoother.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
a design system is a set of building blocks and standards that help keep the look and feel of products and experiences consistent. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gbyb49nhm0t495h8wwakph))
|
||||
|
||||
While both are integral to design systems, component libraries focus on UI elements like buttons and input fields, whereas pattern libraries address broader design solutions like navigation flows or data display. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gc0j368sfxwsseakv52kky))
|
||||
|
||||
While often used interchangeably, design systems are more holistic, including coding standards and usability, while a style guide is a subset focusing primarily on visual elements like colors, typography, and imagery. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gc2ge1rj1tzkkmz150837e))
|
||||
> [!note]
|
||||
> Holistic: An approach that considers the entirety of a system or concept rather than focusing on individual components in isolation. In various fields, including medicine, education, and design, holistic perspectives emphasize the interconnectedness and interdependence of elements, advocating for comprehensive solutions that address the whole rather than just parts. This methodology often leads to more effective and sustainable outcomes by recognizing how components influence one another within a larger context.
|
||||
> ---
|
||||
> Styles guides focus only on visuals meanwhile design systems care about usability as a whole
|
||||
|
||||
Design systems support designers by solving for repeatable patterns and freeing them up to solve other challenges. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gd50z8w8q8x5qc40hmx2yk))
|
||||
|
||||
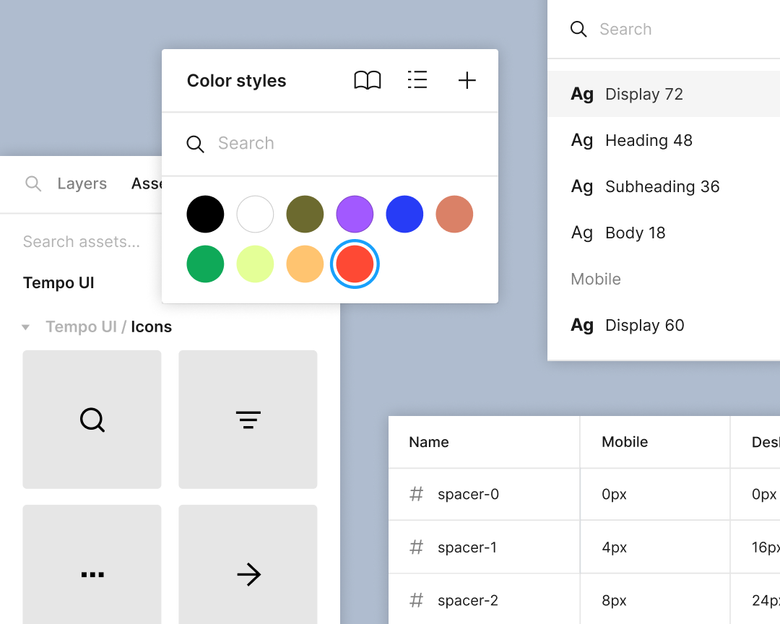 [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gdbmnzscxkqtkbjndqecaa))
|
||||
|
||||
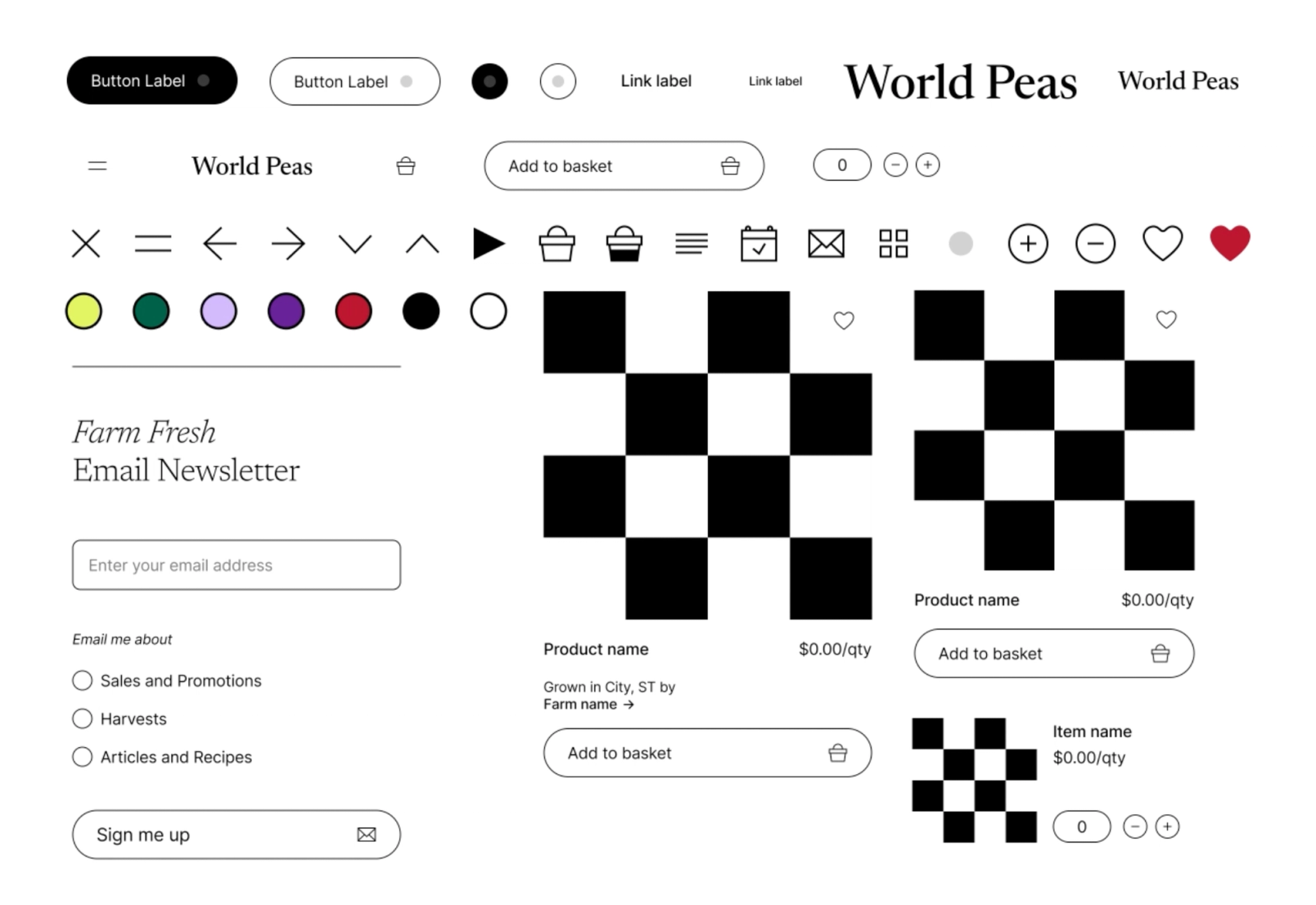 [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7gdbt1d0mvvc58jfhg57t03))
|
||||
|
||||
17
Readwise/Embedded Rust Setup Explained.md
Normal file
17
Readwise/Embedded Rust Setup Explained.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||
# Embedded Rust Setup Explained
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[The Rusty Bits]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Embedded Rust Setup Explained
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TOAynddiu5M
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Embedded%20Rust%20Setup%20Explained
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> The video explains how to set up an environment for embedded software development using Rust. It covers installing the Rust toolchain, configuring VS Code, and compiling code for microcontrollers. The tutorial also discusses debugging techniques and tools needed for embedded Rust projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
to specify a different Target in Rust C is through a Target triple this is composed of a core and sub architecture an
|
||||
optional vendor and or operating system and an environment or AB [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qyvme91v6h3mqqva4s9nm6))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
|||
# How Japanese Minimalism Changed My Life: 5 Principles to Declutter Your Life
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Zach Highley]]
|
||||
- Full Title: How Japanese Minimalism Changed My Life: 5 Principles to Declutter Your Life
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[productivity]]
|
||||
- URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sa7cgPILItQ
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=How%20Japanese%20Minimalism%20Changed%20My%20Life%3A%205%20Principles%20to%20Declutter%20Your%20Life
|
||||
|
||||
> [!note]
|
||||
> **Background:** I will soon be moving out of my parents' house and into a small apartment to live independently. I want to use this transition as an opportunity to embrace a minimalist lifestyle.
|
||||
> ---
|
||||
> ### Top 3 Most Important Takeaways:
|
||||
> 🗑️ **Create Space by Decluttering**
|
||||
> Start by evaluating your physical possessions and ask yourself if each item brings you joy. Embrace the concept of having ample physical space around you, and organize your belongings purposefully. Assign a designated place for every item to prevent clutter from accumulating again.
|
||||
> 🧘 **Eliminate Choices to Free Up Mental Space**
|
||||
> Reduce decision fatigue by minimizing choices in your daily life, such as wearing the same outfit or eating the same meals. Simplifying these decisions will free up mental space and time, allowing you to focus on what truly matters.
|
||||
> 🌿 **Embrace Imperfection and Transience**
|
||||
> Adopt the principle of Wabi-sabi, which encourages finding beauty in imperfection. Understand that nothing is perfect and that everything is transient. This mindset will help you appreciate the simplicity and clarity that comes with minimalism.
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> When there is too much clutter, you can't think. When you can't think, you can't create. When you can't create, your world slows down. What if we only filled our lives with things that had real value and removed everything else.
|
||||
|
||||
📜 Write Up - https://zhighley.com/japanese-minimalism-five-principles-to-declutter-your-life/
|
||||
📸 Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/zachhighley/
|
||||
🐧 Twitter - https://twitter.com/zachhighley
|
||||
💌 Newsletter - https://zhighley.com/newsletter/
|
||||
|
||||
——————————————————————————————————————————————————
|
||||
Who am I:
|
||||
|
||||
My name is Zach. I’m a Resident Physician in Boston. I make videos about medical school, studying, and growth. I love trying new things and often mess up. However, every time I screw up, I usually learn something. Whatever I learn, I post it either on YouTube or on my website 🌐 (https://zhighley.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
I write a weekly newsletter 💌 (https://zhighley.com/newsletter/) linking the best things I read, watched, and listened to that week. Join the 4,000+ that read it every other Sunday...
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
When there's too much stuff around us, our minds can't think straight. When your mind can't think straight, you can't create. When you can't create, when you can't contribute to the world, the world slows down a little bit. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7105sy62k477j7we49j3vng))
|
||||
|
||||
tip number one is create space. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710802fzkm0xb0jfvpe6zj0))
|
||||
|
||||
Marie Kondo says, "When people revert to clutter no matter how much they tidy, it is not their room or their belongings, but their way of thinking that is at fault." [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j71087j6npx5etywvmh93dq4))
|
||||
|
||||
Tip number two is embrace space. Embrace this newfound clearness you have. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j71097tmgwwthqw40kqjm70e))
|
||||
|
||||
Seneca says, "It's not the man who has too little, but the man who craves more who is poor." [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710ans5zjy9p4e10chdkk7b))
|
||||
|
||||
Tip number three is to be purposeful with your space fillers. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710eehmhsxrv02rbrkfxzp3))
|
||||
|
||||
"The reason every item must have a designated place is because the existence of an item without a home multiplies the chances that your space will become cluttered again. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710fafawb9z9265r7r036pv))
|
||||
|
||||
Tip number four is to eliminate choices. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710k01a20dk494w8yf8vq3w))
|
||||
|
||||
When you eliminate decisions, you create more time. Confucius said that, "Life is really simple. We insist on making it complicated." [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710mjajf9x11sk2gy3h4tbm))
|
||||
|
||||
Eliminate decision fatigue, eliminate choices, free up mental space, free up time to focus on things that have a real impact. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710nn39sxpz7md9mhd4cx3q))
|
||||
|
||||
this comes to the important principle of Japanese minimalism of Wabi-sabi or kinda loving imperfection. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710xzs42s3dj7czt7py85qc))
|
||||
|
||||
Tip number six is to think beyond stuff. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j710zgdawxb9bzxj4w5g67p8))
|
||||
|
||||
Create space by decluttering your physical possessions.
|
||||
Does this item give me joy? Embrace space by having as much physical space around you wherever you live. Organize all the things in your life purposely. What is this drawer for? What is this cabinet for? Eliminate choices. Maybe you wear the same outfit every day maybe you eat the same breakfast every day. Maybe you only drink water. Next, everything is transient. Nothing is perfect, and that's okay. And finally, can we apply the idea of simple living to not only our stuff, but our thoughts and our actions. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7117z1262k0pwpp24knqea4))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||
# Practical Concurrency in Go - GoRoutines, Mutexes, Channels and More
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[eldr-io]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Practical Concurrency in Go - GoRoutines, Mutexes, Channels and More
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[dev]] [[dev/go]]
|
||||
- URL: https://youtube.com/watch?v=X24qXb4uWms&si=rsxeM5e_FgY5RCIg
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Practical%20Concurrency%20in%20Go%20-%20GoRoutines%2C%20Mutexes%2C%20Channels%20and%20More
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> The video tutorial demonstrates how to create a concurrent currency exchange API using Go. It explains how to fetch currency rates simultaneously by utilizing goroutines and channels. The goal is to efficiently manage multiple API calls to retrieve currency data.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
We don't really want to spin up a thousand threads just to do API calls. What we want instead is we want a worker pool of threads that can basically, whenever they're available, pick up work, and then they can do the work and then return a result, and then they can pick up the next work until there's no more work to be done. And this is a great pattern called a worker pattern or worker pool pattern. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7ngcdm7y0mhae1x7a524k9q))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
|||
# Remember Everything With This Pocket Notebook System
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Eric Pfohl]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Remember Everything With This Pocket Notebook System
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[notetaking]]
|
||||
- URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=swC4MAryYRw
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Remember%20Everything%20With%20This%20Pocket%20Notebook%20System
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> A Commonplace Notebook is a helpful tool for collecting and organizing ideas, quotes, and details from various sources like books and podcasts. It allows you to document wisdom in one place, making it easier to reference later. Using pen and paper for this process can enhance your memory and creativity.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
a Commonplace Notebook is a way to collect details around you that are relevant to you in some way rather than writing things down introspectively like a diary or Journal would be a Commonplace Notebook is a way to document things only from external sources [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j70zaykjztys0bef0xp5ef4e))
|
||||
|
||||
they allow you to document and collect any ideas in a singular place that you can refer back to at any time [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j70zcrej9xvmp5905czk027r))
|
||||
|
||||
if you're somebody like me who likes organization the thought of just a bunch of random ideas on the pages seems a little bit overwhelming and messy but honestly the organization of your Commonplace Notebook is nothing to worry about our thoughts ideas and minds are constantly going in a million different directions and realistically your Commonplace Notebook is going to be an extension of
|
||||
that [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j70zkh7h2rtdjrptg01f854g))
|
||||
|
||||
one way to do this is to leave the first page or two of your notebook blank so that way when you fill the notebook you can put an index on those blank pages [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j70znccjr4srj337fdjqmw79))
|
||||
|
||||
you can highlight certain categories in specific colors or you can even write in different colored inks depending on the topic [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j70zp3p890b8kdqx21w2gqm8))
|
||||
|
||||
with a Commonplace Notebook I do think is a great idea to collect your observed details and expand upon them further through writing [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j70zrzc6s2g9x9768b2596qa))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
# Sharing Code Between Projects: Lessons Learned in the Trenches
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Smashing Magazine]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Sharing Code Between Projects: Lessons Learned in the Trenches
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- URL: https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2018/04/sharing-code-between-projects/
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Sharing%20Code%20Between%20Projects%3A%20Lessons%20Learned%20in%20the%20Trenches
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> Jonathan Saring discusses the challenges of sharing code between projects and the lessons learned by his team. They found that code duplication was widespread and sought a better way to share components without the complexities of multiple repositories or libraries. This led to the creation of Bit, a tool that simplifies code sharing and collaboration across projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
Trying to publish a few files from our project to NPM forced us to split our repository and create new ones just to share this code. When dealing with hundreds of components, **this meant having to maintain and make changes across hundreds of repositories**. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7c7r70prgze7nhnwf9mrvyb))
|
||||
|
||||
Even then, we had now a simple way to organize these packages and make them easily [discoverable](https://medium.com/@Rich_Harris/small-modules-it-s-not-quite-that-simple-3ca532d65de4#.88d5anyhv) to our entire team. Another major problem was the coupling between the packages and the owners of their origin repositories, which made it nearly impossible for other people to quickly make updates to the packages while working on their own projects. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7c7snv6bz7w24x6v99zar37))
|
||||
|
||||
Choosing this option meant we would still have to effectively keep multiple packages with multiple `package.json` files, multiple build and test environments and a complicated dependency tree to handle between them. Updating these packages must also go through the main repository, still making it hard to modify these package from other projects when working with a few separate monorepos. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7c7tyqzf8z4ns8sr35gstvb))
|
||||
|
||||
This option was quickly dropped, too. In a lot of way, it resembles using a CD-ROMs instead of an iTunes playlist. First, it made no sense to force an entire library of React components and an entire utility library and so on on each of our projects.
|
||||
Secondly, every project using it would be tightly coupled to the development of this library, making it impossible to adjust its components for each project. This becomes most painful when sharing common Node.js code between our microservices, which would now be coupled to the library.
|
||||
Thirdly, discoverability within the library is bound to be poor and would involve a lot of work with its documentation and usage in different edge cases. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7c7x4br1vpa6peckn8f04x1))
|
||||
|
||||
You there. You're thinking about using a Git submodule. DON'T. Just don't. It's not worth it, ever.
|
||||
— Jeremy Kahn (@jeremyckahn) [December 16, 2012](https://twitter.com/jeremyckahn/status/280406794583539712?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw) [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7c7zhs027w5jac3mg71v905))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
|||
# Stateful vs. Stateless Applications — Differences, Pros & Cons, Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Neal Davis]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Stateful vs. Stateless Applications — Differences, Pros & Cons, Use Cases
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- URL: https://neal-davis.medium.com/stateful-vs-stateless-applications-differences-pros-cons-use-cases-ad4b434576b8
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Stateful%20vs.%20Stateless%20Applications%20%E2%80%94%20Differences%2C%20Pros%20%26%20Cons%2C%20Use%20Cases
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> Stateful applications remember user interactions and store data between sessions, while stateless applications do not retain any user information. This choice affects how applications are designed, their scalability, and the resources they require. Developers must weigh the pros and cons of each type to meet their project needs effectively.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
Stateful applications save info about the user’s “state” by keeping track of what they do. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7pd95t5qyvwt98kv86bmcbf))
|
||||
|
||||
Stateless software applications are those applications that do not save information about previous interactions, user sessions, or events. These applications do not preserve context or state between requests in a stateless design. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7pdbyyxz2g1ems20te5d6ez))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
|||
# The Purest Coding Style, Where Bugs Are Near Impossible
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Coderized]]
|
||||
- Full Title: The Purest Coding Style, Where Bugs Are Near Impossible
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[dev]] [[dev/design-patterns]]
|
||||
- URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HlgG395PQWw
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=The%20Purest%20Coding%20Style%2C%20Where%20Bugs%20Are%20Near%20Impossible
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> Functional programming is a coding style that emphasizes using functions and avoiding side effects to create more reliable and maintainable code. It promotes concepts like immutability and closures, which help keep data and functions organized. While it can be complex, learning functional programming can enhance your coding skills, regardless of your background.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
we have imperative, or the paradigm of giving explicit instructions.
|
||||
Basically, the "how." And declarative, or the paradigm of describing our goals. Basically, the "what." [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qxkzfnjbsj5k63874xp5cm)) [[dev/design-patterns]] [[dev]]
|
||||
|
||||
At the core of the functional paradigm, we have functions, obviously. And these functions need to be usable in a fairly unrestricted way ... we can pass them to other functions and return them from other functions,
|
||||
as well as hold references to them for later use. ... We also need to be able to create closures, which are functions that can access and remember the scope around them.
|
||||
|
||||
"A closure is a poor man's object... ...and an object is a poor man's closure." [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qxw02q306dmkqttpc9phze))
|
||||
|
||||
higher-order functions, which are functions that work with other functions to perform an action. Think filter(), sort(), map(), and so on. These help us create reusable and isolated modules [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qxwvqq86xrr3rvagas3mb2))
|
||||
|
||||
we have immutability, where we aim to avoid something called side effects. Side effects happen when we allow unpredictable state from outside the scope of a function to affect it in some way, or when we allow a function to make changes outside of its scope. By getting rid of potential side effects, our functions become pure, in that if the same data goes into a function, we can always guarantee the same result coming out, without affecting anything else. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qxz3ra928rvfavgendb12z)) [[c1]]
|
||||
|
||||
Currying brings multiple arguments of a function into their own function calls that we then chain together.
|
||||
It achieves this using the memory scope ability of closures, where each argument stays in memory until the chain completes, and we get our result. In a similar way, we can use closures to create something resembling an object. The first function in the chain acts as a kind of object constructor, and is where we define most of our internal data. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qy48epfjav6h7rtv8a3nxa))
|
||||
|
||||
Currying brings multiple arguments of a function into their own function calls that we then chain together.
|
||||
It achieves this using the memory scope ability of closures, where each argument stays in memory until the chain completes, and we get our result. In a similar way, we can use closures to create something resembling an object. The first function in the chain acts as a kind of object constructor, and is where we define most of our internal data. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qy688qvfwj8asj84mzz9t6))
|
||||
|
||||
Currying brings multiple arguments of a function into their own function calls that we then chain together.
|
||||
It achieves this using the memory scope ability of closures, where each argument stays in memory until the chain completes, and we get our result. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qy6nkgytf7x78h6mq3jqts))
|
||||
|
||||
we can use closures to create something resembling an object. The first function in the chain acts as a kind of object constructor, and is where we define most of our internal data.
|
||||
This data is privately scoped to the constructor function and is therefore encapsulated by it. We can then return a closure to provide external access to this private data. ... we can go as far as returning multiple named closures to access and manipulate the internal data in more complex ways, further solidifying its object-like behaviors.
|
||||
|
||||
In the purely functional paradigm, we work primarily with types and expressions, where the following rules apply: Code is generally evaluated rather than executed, which gives us some interesting new optimization capabilities, such as lazy evaluation and automatic parallelization. Immutability is enforced everywhere, meaning that when we want to make changes to our data,
|
||||
We do so by computing a new constant based on an existing constant. And to keep functions pure, the mere thought of a side effect is punishable by the most horrific torture imaginable. Having to learn... MONADS! [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qyccaq27vqjn4wqabpsdd5))
|
||||
|
||||
The immutability of the functional paradigm forces us to think more strictly about how we pass data around, helping to ensure that changes don’t happen unexpectedly. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qyec9pb8pmxcegkbrnj5d2))
|
||||
|
||||
guides us in forming readable code that is highly modular and therefore maintainable. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qyeqqgmbv2v8wk6m1a0fz1))
|
||||
|
||||
It does come at the cost of potentially being a bit harder to optimize [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7qyf3kdvtrsnvdfnm7hf6fq))
|
||||
|
||||
46
Readwise/TypeScript the Right Way.md
Normal file
46
Readwise/TypeScript the Right Way.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
|||
# TypeScript the Right Way
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Awesome]]
|
||||
- Full Title: TypeScript the Right Way
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[dev]] [[dev/javascript]]
|
||||
- URL: https://youtube.com/watch?v=UMEp6eFU16k&si=5FrI-L7etAUGFl1K
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=TypeScript%20the%20Right%20Way
|
||||
|
||||
> [!note]
|
||||
> **Background:** I want to incorporate TypeScript in my projects to enhance code quality, readability, and maintainability while ensuring type safety.
|
||||
> ### Top 3 Important Takeaways or To-Dos:
|
||||
> 🛠️ **Keep Types Simple:** Avoid using nested types, complex unions, and intersections. Overcomplicated types can lead to confusion and higher maintenance costs, so aim to maintain simplicity in your type definitions.
|
||||
> 🔍 **Utilize Type Guards:** Implement type guards to check for null or undefined values before using variables. This practice enhances code safety and reliability by ensuring that variables are properly validated.
|
||||
> 🚫 **Avoid Using "Any":** Steer clear of the "any" type, as it defeats the purpose of type safety in TypeScript. Instead, use union types, type guards, or the unknown type to handle uncertain variable types effectively.
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> TypeScript has become popular for modern web development because it improves upon JavaScript's weaknesses. It adds static type checking, helping developers catch errors before their code runs. Following best practices in TypeScript, such as avoiding overly complex types, ensures safer and more maintainable code.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
Let’s say you have a basic function that adds up two numbers in a main.js file. In pure JavaScript there isn’t anything stopping you from passing strings or any other type of object as a parameter to this function. To avoid this, we need that extra layer of validation provided by TypeScript. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r04ptybp6b904wk49qar0a))
|
||||
|
||||
the first rule should be pretty obvious - avoid using the “any” type at all costs. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r07sqy58gkbmcg2n0kg1tv))
|
||||
|
||||
there will be those corner case scenarios where you don’t really know the shape of an object ... In such scenarios don’t hesitate to use union types and type guards to make your code safer. If you are truly unsure of a variable's type, you could use the unknown type instead of any or leave out the type reference to allow TypeScript to infer it.
|
||||
|
||||
remember to avoid overly verbose type annotations when they are unnecessary. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0c9r7ws816nrtcmbksehf))
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript offers a strict mode compiler option that enforces more rigorous type checking and constraints to enhance code quality and to catch potential issues during development. You can enable this by setting the strict flag to true in the TS config file. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0dn8e90zkxvdj370t22tw))
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript’s strict mode was introduced in ES 5 and you should always use it as well. This will allow you to opt in to a restricted variant of JavaScript where silent errors are changed to throw errors, some mistakes that make it difficult for the engine to perform optimizations are fixed, and syntax likely to be defined in future versions is prohibited. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0f8r2nskx1jagx6sn7hsf))
|
||||
|
||||
A type alias creates a new name for a type. This can be a primitive, union, intersection, tuple or any other type. In other words it can represent complex structures and give you flexibility in defining types that go beyond simple object shapes. On the other hand, interfaces are primarily used to define the structure or shape of an object or class. Interfaces in TypeScript are more focused on describing the properties and methods that an object should have,
|
||||
and they provide a powerful way to enforce the structure of objects across your codebase. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0hfyz8nps371dqga3bmmh))
|
||||
|
||||
you should use interfaces for object shapes and class contracts, use types for complex and flexible structures and use a combination of both to create powerful type definitions. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0jedxp5gd3h5qpkr428v0))
|
||||
|
||||
Non-Nullable assertions are Another big source of potential problems since they can lead to runtime errors if used incorrectly. ... you should use type guards to ensure that variables are properly checked for null or undefined values before use. This approach leads to safer and more reliable code.
|
||||
|
||||
keep things simple.
|
||||
Overcomplicated types are a common pitfall in TypeScript projects, and although complex types may occasionally be needed, making them overly complicated can result in confusion, reduced readability, and higher maintenance costs. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0pctvv439x5ev9w1ccz74))
|
||||
|
||||
Avoid nested types since they are hard to read and maintain, avoid complex union and intersection types since they can lead to convoluted and difficult-to-understand types, and don’t overuse mapped and conditional types since they can easily get over complicated. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7r0rw8djwydvfy9jdx0e8wj))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
# Understanding Composition in Software Development
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Hamida Meknassi]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Understanding Composition in Software Development
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[dev]] [[dev/design-patterns]]
|
||||
- URL: https://medium.com/@hamida.meknassi/understanding-composition-in-software-development-74f84ab984ce
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Understanding%20Composition%20in%20Software%20Development
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> Composition is a software development principle that emphasizes building complex systems by combining smaller, independent components rather than using inheritance. This approach offers flexibility, reusability, and easier maintenance, making it a popular choice among developers. By favoring composition, developers can create more adaptable and manageable systems.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
At its core, composition is about constructing complex systems by piecing together smaller, distinct objects. In object-oriented programming lingo, we often describe it as a “has-a” relationship rather than the “is-a” relationship that comes with inheritance. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jxtrsfs087rbx45dgh9skx))
|
||||
|
||||
Flexibility : As requirements change, it’s easier to swap or upgrade individual components without disrupting the entire system.
|
||||
Reusability : Crafted correctly, components can be used across various parts of a project or even in entirely different projects.
|
||||
Maintainability : Focused and modular components are easier to understand, test, debug, and enhance.
|
||||
Reduced Side Effect : Unlike inheritance, where modifying the base can have widespread consequences, composition limits the ripple effect of changes. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jxvsqhk5j1bzjarjrwymhr))
|
||||
|
||||
When facing a complex problem, ask:
|
||||
- Which components make up this system?
|
||||
- How can I break this down into smaller, more manageable pieces?
|
||||
- Can I reuse existing components? [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jxxp9dp3sqncv2d9rewnqs))
|
||||
|
||||
53
Readwise/Why Composition Is Often Better Than Inheritance.md
Normal file
53
Readwise/Why Composition Is Often Better Than Inheritance.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
|||
# Why Composition Is Often Better Than Inheritance
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata
|
||||
- Author: [[Joost van Dongen]]
|
||||
- Full Title: Why Composition Is Often Better Than Inheritance
|
||||
- Category: #articles
|
||||
- Document Tags: [[dev]] [[dev/design-patterns]]
|
||||
- URL: https://joostdevblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/why-composition-is-often-better-than.html
|
||||
- Archive: https://web-archive.alecodes.page/bookmarks?bf=1&search=&title=Why%20Composition%20Is%20Often%20Better%20Than%20Inheritance
|
||||
|
||||
> [!note]
|
||||
> Por lo que entiendo de momento:
|
||||
> - Usar composition by default unless you have a reason to use inheritance
|
||||
> - Permite crear código más reutilizable y más _"loosly coupled"_, en donde es más dificil que cambios en una parte del código afecten a otra
|
||||
> - Composition puede estar relacionado con [[dependency injection]] pero no estoy del todo seguro
|
||||
> - Razones para usar herencia pueden ser:
|
||||
> - [[polymorphism]], para crear variantes con una interfaz común
|
||||
> - Ciertos patrones de diseño como [[factory]] y [[listener]]
|
||||
> [!tldr]
|
||||
> The article argues that using composition is often better than inheritance in code structure. While inheritance can seem more natural, composition offers greater flexibility, readability, and reduces the risk of bugs. The author suggests that developers should be cautious with inheritance and consider composition for many situations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Highlights
|
||||
the famous *diamond problem*. What happens when a class A inherits from two classes B and C that both inherit from a single parent D? A now has a D twice and chaos ensues. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7k02e4exj8srkx4242fpxkj))
|
||||
|
||||
The problem is that when it does, it can often be very difficult to come up with a good solution for how to get rid of it without doing a lot of refactoring. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7k01q1m9fafymhnjn692hgk))
|
||||
|
||||
Inheritance is very useful for a lot things, for example in polymorphism and in design patters like listeners and factories. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7k03r10m6ncdmpn301yc0ns))
|
||||
|
||||
An important question in code structure is whether to make classes work together through composition or inheritance. The "has a" relationship versus the "is a" relationship. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jy5adbxd6hqanwamxwyr34))
|
||||
|
||||
In my experience intuition often favours inheritance, but it gives so many problems that in many cases composition is better. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jy705wznt9rph7nxb66r4n))
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see in this code, CharacterInheritance is shorter. It also feels more natural, since we don't have to write these extra accessor functions for *applyKnockback* and *getPosition*. However, after years of creating both of these kinds of structures I have learned that in a situation like this, using composition is actually more flexible, less sensitive to bugs and even more understandable than using inheritance. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jyaz1nx8p671tzccsgqx29))
|
||||
|
||||
Game designers constantly come up with game mechanics that are exceptions to what you already programmed. Saying no to these just because your code structure cannot handle them will seriously damage your game quality [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzcahqza5zye0dxa3yxvdx))
|
||||
|
||||
An important goal in game programming is flexibility: making your code in such a way that it is relatively easy to add whatever weird whim the game designers come up with today. In most cases composition is much more flexible than inheritance. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzdzcr2kv4qtdp378h2chd))
|
||||
|
||||
"Readability" is always accomponied by "sensitivity to bugs", since if a programmer does not really understand how something works, then he will likely break it when working on it. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzem4sqbhqgzj1z7cqm7vx))
|
||||
|
||||
*virtual* and *protected* functions. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzm6wg5dwhd71cmtv7ehzb))
|
||||
> [!note]
|
||||
> **Virtual and Protected Functions**: In object-oriented programming, *virtual functions* are member functions in a base class that can be overridden in derived classes. They enable polymorphism, allowing the correct function to be called based on the object's runtime type rather than the type of reference or pointer. This is crucial for implementing dynamic behavior in applications.
|
||||
> *Protected functions*, on the other hand, are member functions that can be accessed within their own class and by derived classes, but not by outside classes. This access control mechanism helps encapsulate the functionality of a class while still allowing derived classes to utilize or extend that functionality. Together, virtual and protected functions facilitate code reuse and maintainability in complex software systems.
|
||||
|
||||
inherited classes work together to create complex behaviour and intertwine more and more over time. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzh52x8t0pgefbgzdktpay))
|
||||
|
||||
this is just too much code to really grasp it all at once without starting to mix things up. The result is that readability decreases and the programmer becomes more likely to introduce bugs because she overlooked something. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzkaftyev2f34t5x6k5n43))
|
||||
|
||||
This keeps the classes from intertwining over time and makes it easier to keep them truly separate. [View Highlight](https://read.readwise.io/read/01j7jzr2x12ncezqhzp3r1qr3h))
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue